views
Introduction
Beneficial insects play a vital role in sustainable agriculture, ecological balance, and pest management. These insects serve as natural predators, pollinators, and decomposers, contributing significantly to crop productivity and ecosystem health. With increasing concerns about the adverse effects of synthetic pesticides on human health, the environment, and non-target organisms, the demand for beneficial insects has gained substantial momentum across the globe. Beneficial insects not only help reduce chemical pesticide usage but also ensure long-term soil fertility, improve crop resilience, and support biodiversity.
Farmers, agro-industrialists, and policymakers are increasingly recognizing the potential of integrating biological control agents, including beneficial insects, into integrated pest management (IPM) programs. Rising environmental awareness and strict regulations on chemical pesticide usage have opened lucrative opportunities for the beneficial insects market.
Source: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-beneficial-insects-market
The Evolution
The use of beneficial insects dates back to ancient civilizations when farmers observed natural pest control mechanisms and selectively promoted helpful insects in their fields. However, the concept of biological control began to formalize in the late 19th and early 20th centuries with scientific studies and controlled releases of natural enemies to combat pest outbreaks.
One of the most notable early examples is the successful introduction of the Vedalia beetle in California in the late 1800s to control cottony cushion scale infestations in citrus orchards. This success marked the beginning of classical biological control practices globally. Over the decades, researchers and entomologists expanded their understanding of predator-prey dynamics, leading to the development of more systematic biological control programs.
During the second half of the 20th century, the agricultural industry became heavily reliant on synthetic pesticides, sidelining biological control agents. However, pesticide resistance, environmental degradation, and consumer demand for chemical-free food revived interest in beneficial insects.
In the early 2000s, the integration of beneficial insects into integrated pest management (IPM) programs gained momentum. Technological advancements, including controlled mass-rearing of beneficial insects, insect packaging innovations, and delivery systems, made biological control more practical and commercially viable. Today, beneficial insects are an essential component of modern sustainable farming practices worldwide.
Market Trends
Several trends are shaping the beneficial insects market and driving its rapid growth.
Rising Demand for Organic and Sustainable Agriculture
Consumer preference for organic, pesticide-free, and sustainably produced food is fueling demand for biological pest control. Organic farming strictly prohibits or limits the use of synthetic pesticides, creating significant market opportunities for beneficial insects.
Government Regulations Favoring Biological Control
Regulatory bodies worldwide are enforcing stricter rules on chemical pesticide usage due to health and environmental concerns. Governments are encouraging farmers to adopt eco-friendly pest control methods by providing financial incentives, subsidies, and training programs promoting the use of beneficial insects.
Advances in Mass Production and Delivery Systems
Improvements in insect mass-rearing technologies and packaging systems have made it easier for producers to deliver high-quality, viable beneficial insects to end-users. Innovations such as slow-release sachets, drones for insect distribution, and temperature-controlled packaging have enhanced field performance and reduced post-production losses.
Increasing Adoption of Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM programs are becoming standard practice among commercial growers due to their ability to balance pest control, yield optimization, and environmental sustainability. Beneficial insects are integral to IPM programs, as they reduce the need for chemical inputs and offer sustainable long-term solutions.
Growing Application Beyond Agriculture
Beneficial insects are now being used beyond traditional agriculture in applications such as horticulture, floriculture, urban landscaping, forestry, and greenhouse farming. Their versatility is expanding their market footprint in urban gardening, botanical gardens, and controlled-environment agriculture (CEA).
Rising Investments in Biological Control Companies
The increasing demand for sustainable agriculture has attracted investments from private equity, venture capital, and multinational agribusinesses. Companies specializing in beneficial insects and biological pest control are expanding their product portfolios and geographical reach through mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships.
Challenges
Despite the promising growth, the beneficial insects market faces several challenges.
High Initial Investment
The cost of setting up beneficial insect production facilities and implementing biological control programs is higher than conventional chemical pesticide-based approaches. For small-scale farmers, the upfront costs can act as a deterrent.
Limited Shelf Life
Beneficial insects are living organisms with a limited shelf life. Proper storage, transport, and handling are required to maintain their viability. Inadequate supply chain infrastructure, particularly in developing regions, affects product quality and limits market penetration.
Specificity of Insect-Pest Interaction
Beneficial insects often target specific pests. If pest identification is incorrect or if multiple pest species infest a crop simultaneously, biological control may not provide comprehensive protection without supplementary measures.
Climate Sensitivity
Temperature, humidity, and weather conditions affect the survival and performance of beneficial insects. In unfavorable climates, their efficacy may be reduced, requiring farmers to invest in supplementary pest control methods.
Lack of Awareness
In many regions, especially in developing countries, awareness about the benefits and practical implementation of biological pest control remains limited. Farmer education and extension services are crucial to overcoming this barrier.
Regulatory Hurdles
While regulations favor reduced pesticide use, the registration and approval of biological control agents in some countries can be complex and time-consuming. Navigating regulatory requirements is often a challenge for new market entrants.
Market Scope
The beneficial insects market serves various segments across agriculture, horticulture, and landscaping. Its reach is expanding beyond developed countries into emerging economies.
Crop Scope
Beneficial insects are used in the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, cereals, oilseeds, pulses, ornamental plants, and greenhouse crops. Fruit and vegetable production accounts for the largest share due to the high value of these crops and their vulnerability to insect pests.
Type Scope
The market is segmented into:
-
Predatory insects (lady beetles, lacewings, predatory mites)
-
Parasitoids (parasitic wasps)
-
Pollinators (honeybees, bumblebees)
-
Decomposers and others
Predatory insects dominate the market due to their effectiveness against a wide range of pests such as aphids, whiteflies, mites, and thrips.
Regional Scope
Europe and North America lead the market due to early adoption of sustainable agricultural practices, government regulations, and advanced infrastructure. The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing significant growth due to increasing food demand, awareness about organic farming, and government initiatives promoting biological control.
Latin America, driven by its large agricultural base, and the Middle East & Africa, driven by food security concerns, represent emerging markets with high growth potential.
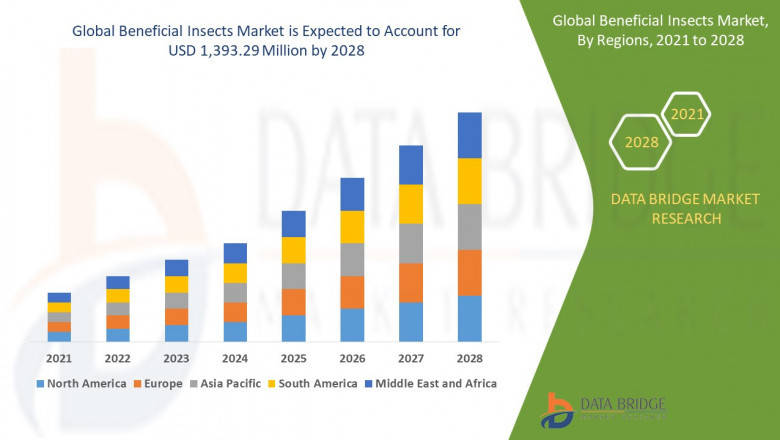
Market Size
The global beneficial insects market was valued at approximately USD 750 million in 2024 and is expected to surpass USD 1.7 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12% during the forecast period.
Europe accounts for nearly 40% of the market share due to its stringent pesticide regulations and well-established organic farming sector. North America follows closely, supported by the adoption of IPM programs and the growing organic food industry.
The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate due to increasing organic farming practices, rising awareness, and government support. The region's large and diverse agricultural landscape provides significant opportunities for the expansion of beneficial insect usage.
Factors Driving Growth
Multiple factors are propelling the growth of the beneficial insects market.
Growing Demand for Organic Produce
Consumer preference for organic, residue-free food products is driving the adoption of sustainable farming practices globally. Beneficial insects serve as a natural alternative to chemical pesticides, aligning with the organic farming philosophy.
Environmental Concerns and Regulatory Support
Stringent regulations limiting chemical pesticide usage and growing awareness about the environmental impact of conventional pest control methods are accelerating the adoption of biological control agents.
Advancements in Insect Mass Production
Technological improvements in the mass production, packaging, and delivery of beneficial insects have lowered production costs and improved field performance, making biological control more accessible to farmers.
Increasing Pesticide Resistance
Pests have developed resistance to several chemical pesticides, rendering them ineffective. Beneficial insects offer a sustainable and effective alternative that avoids resistance buildup.
Expansion of IPM Programs
The rising popularity of integrated pest management practices is creating a favorable environment for the use of beneficial insects as an essential component of holistic pest control.
Investment and Innovation
Growing investments by both public and private sectors in biological control companies are fostering innovation, expanding product portfolios, and supporting market expansion.
Rising Food Security Concerns
With the global population rising, there is an increasing focus on sustainable food production. Beneficial insects help improve crop yields without compromising environmental health, addressing the dual challenge of food security and sustainability.













Comments
0 comment